Solar panels in England will generate between 15-27% as much electricity in the winter compared to their summer peak, depending on the direction they face, pitch and shading. North facing solar panels will produce just 6% compared to the energy generated in their summer peak.
How much electricitiy do solar panels generate in the winter compared to other times of the year?
Using real case studies with South/East/West & North roof faces.

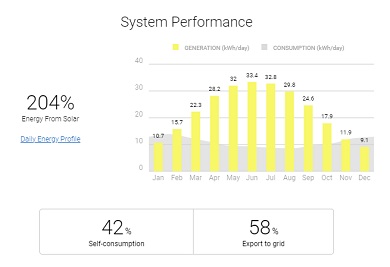
In December this array will generate 27% of the amount of electricity it would produce in June.
Direction: North. Location: Hove, East Sussex. Pitch: 30 degrees

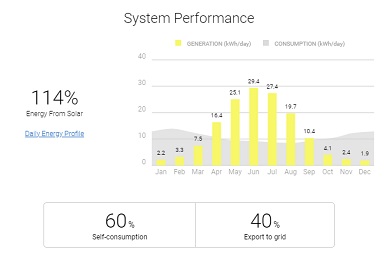
In December this array will generate just 6.4% of the amount of electricity it would generate in June.
Direction: West. Location: Hove, East Sussex. Pitch: 30 degrees

In December this array will generate 15% of the amount of electricity it would produce in June.
Direction: East. Location: Hove, East Sussex. Pitch: 30 degrees


In December this array will generate 13.5% of the amount of electricity it would produce in June.
Conclusion
How much will solar panels generate in the winter? It depends mostly on the direction and pitch.
We can see that the further away from South facing the less the array will generate in the winter as a percentage of it’s summer peak. Ranging from around 15% for East and West facing roofs to around 27% for a South facing roof. A North-facing roof will produce just 6% of the energy compared to it’s summer peak.
Interesting points.
Look at the shape of the production charts for each solar panel system, it may be surprising to see that a North-facing roof generates as much as 88% of the energy a south-facing roof in the summer but far less in the winter at just 21% of the generation of the same south-facing roof.
East and West facing roofs should be very similar. The electricity produced during the time of day will be different – with East facing roofs generating more before midday and West facing roofs generating more in the afternoon.
The production graphs above illustrate how direction influences the shape of energy production throughout the year. The further away from South – the steeper the production graph, comparatively higher amounts of energy generated in the summer compared to lower levels in the winter.
Pitch acts to enhance the direction of the solar panels.
If we imagine that a flat roof (0 degree pitch) is facing equally South, East, West and North, then increasing the pitch will emphasise the direction it faces.
For example, a solar array on a flat roof at 0 degrees will be facing equally South, East, West and North.
Increase the pitch to 30 degrees and you will have made a choice on which direction the solar array faces. The array now favours one direction and is pointing away from the opposite direction.
Shading changes throughout the year as the sun moves higher and lower in the sky. You may not have any shade during the summer, but a longer shadow may cause shade in the winter, which can affect generation.












